MESOTHELIOMA CANCER SYMPTOMS.
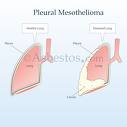
The early symptoms of mesothelioma are generally non-specific, and may lead to a delay in diagnosis. Sometimes resembling viral pneumonia, pleural mesothelioma patients may present with shortness of breath, chest pain and/or persistent cough; some patients show no symptoms at all. A chest x-ray may show a build-up of fluid or pleural effusion (discussed below). The right lung is affected 60% of the time, with involvement of both lungs being seen in approximately 5% of patients at the time of diagnosis. Less common symptoms of pleural mesothelioma include fever, night sweats and weight loss. Symptoms of peritoneal mesothelioma may include pain or swelling in the abdomen due to a build-up of fluid, nausea, weight loss, bowel obstruction, anemia or swelling of the feet. PLEASE KEEP IN MIND THAT THESE SYMPTOMS MAY BE CAUSED BY MESOTHELIOMA OR BY OTHER LESS SERIOUS CONDITIONS. ONLY A DOCTOR CAN MAKE A DEFINITIVE DIAGNOSIS Pleural EffusionOne of the most common symptoms of mesothelioma is a pleural effusion, or an accumulation of fluid between the parietal pleura (the pleura covering the chest wall and diaphragm) and the visceral pleura (the pleura covering the lungs). Both of these membranes are covered with mesothelial cells which, under normal conditions, produce a small amount of fluid that acts as a lubricant between the chest wall and the lung. Any excess fluid is absorbed by blood and lymph vessels maintaining a balance. When too much fluid forms, the result is an effusion. TypesPleural effusion is broken down into two categories, transudates and exudates. A transudate is a clear fluid that forms not because the pleural surfaces are diseased, but because of an imbalance between the normal production and removal of the fluid. The most common cause of transudative fluid is congestive heart failure. An exudate, which is often cloudy and contains many cells and proteins, results from disease of the pleura itself, and is common to mesothelioma. To determine whether a fluid is a transudate or exudate, a diagnostic thoracentesis, in which a needle or catheter is used to obtain a fluid sample, may be conducted. A patient with mesothelioms often demonstrates symptoms 15 to 50 years after initial exposure to asbestos. The cancer may take decades to develop in the body and symptoms do not arise until after the cancer is present. Many patients are unaware of the severity of their condition since mesothelioma symptoms typically resemble symptoms of less serious illnesses. What if I have Symptoms of Mesothelioma?If you have a history of asbestos exposure, the leading cause of mesothelioma, and experience any of the symptoms detailed above, it is best to seek immediate medical advice. Informing your doctor of previous asbestos exposure can alert them to the possibility of an asbestos-related disease such as mesothelioma. Also, in the interest of early detection, those who were exposed but have not yet exhibited symptoms should undergo regular chest X-rays or pulmonary function tests to monitor any adverse affects of asbestos inhalation. When a doctor informs a patient of a mesothelioma diagnosis, patients and their loved ones are often very confused since the cancer is relatively unknown. Asbestos.com provides a complimentary packet with comprehensive information about mesothelioma symptoms and next-step guidance following a diagnosis. Pleural Mesothelioma SymptomsPleural mesothelioma is the most common form of the cancer, comprising approximately two-thirds of all mesothelioma cases. Known symptoms of pleural mesothelioma include:
Symptoms of pleural mesothelioma occur as a result of thickening of the pleural membrane, caused by the rapid production of cancerous cells which can lead to the buildup of fluid between membrane layers. Tissue thickening and fluid buildup place pressure on the lungs, leading to reduced respiratory function.
Peritoneal Mesothelioma SymptomsPeritoneal mesothelioma accounts for approximately 25 to 30 percent of mesothelioma diagnoses and symptoms may include:
Symptoms are caused by the thickening of the peritoneal membrane and the resulting build-up of fluid between membrane layers. These changes in membrane composition put pressure on the abdominal region and organs, causing a patient to demonstrate symptoms of the cancer. Pericardial Mesothelioma SymptomsPericardial mesothelioma accounts for less than 5 percent of all mesothelioma. Symptoms are caused by thickening of the pericardial membrane and fluid buildup. Known symptoms include:
Pericardial mesothelioma is so rare that the recognized body of symptoms is not as well-developed as with more common types of mesothelioma. It is a particularly difficult type of mesothelioma to diagnose, and this correlates to a poor prognosis among pericardial mesothelioma patients. Testicular Mesothelioma SymptomsTesticular mesothelioma is an extremely rare form of cancer, as less than 100 cases of testicular mesothelioma have been recorded in the last 60 years. With so few cases recorded, very little is known about the symptoms of this disease. The only known symptom of testicular mesothelioma is the appearance of testicular lumps, and the lumps may or may not be painful. Click here to start typing your text  Custom Search
|